What is Trypsin?
Trypsin is a digestive enzyme known as a protease, secreted by the pancreas that selectively breaks (cleaves) proteins into smaller peptides. It belongs to a large family of enzymes called serine proteases in which the amino acid serine plays a key role in the active site of the enzyme
What is Trypsin’s Role?
Functionally, enzymes are highly specific and targeted in their function. Trypsin specifically cleaves peptides on the C-terminal side of arginine and lysine residues. If there is a proline amino acid on the carboxyl side of the cleavage site, the hydrolysis reaction is stopped and if there is an acidic amino acid residue on either side of the targeted site, the reaction slows down. Trypsin is classified as an endoprotease since it breaks down proteins in the middle of the chain rather than at its ends. The optimal activity of this enzymes is at a pH range between 7 and 9.
Trypsin originates as a larger inactive precursor molecule known as trypsinogen and becomes active through the removal of a small peptide from the N-terminal portion of the protein. This activation step occurs at a neutral pH in the presence of trypsin or another digestive enzyme. In its final, active form, trypsin is a single chain protein comprised of 223 amino acids.
How Does Trypsin Work?
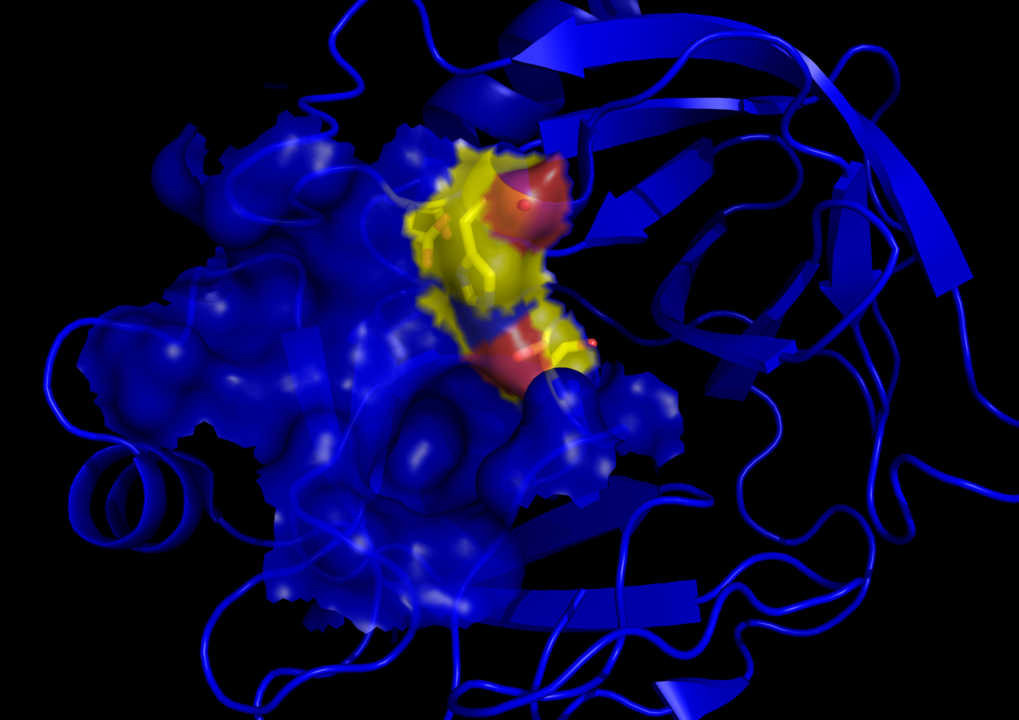
Trypsin functions similarly to other serine proteases. These enzymes contain a ‘catalytic triad, or a specific amino acid three-some including histidine, aspartate, and serine that comprise its active site. The proximity of the histidine and aspartate in relation to serine within the triad, in conjunction with stabilizing forces created by other neighboring amino acids, makes this serine residue able to donate electrons to the protein amide bond. This action results in clipping the amide bond of a specific amino acid sequence containing arginine and lysine residues.
In addition, the negatively charged aspartate residue of the triad is responsible for attracting and stabilizing positively charged lysine and arginine into the catalytic site. This precise charge interaction creates the specificity of the trypsin enzyme for protein sequences containing these unique amino acids.
What is trypsin used for?
Besides playing a critical role in digestion, trypsin has many other applications both in science as well as industry. Examples of common trypsin usage include:
- Breaking down (pre-digesting) tissue for specialty food applications such as the preparation of baby food.
- Resuspending tissue culture cells which adhere to culture vessels, during the process of cell harvesting. During this process of ‘trypsinization’, trypsin digests the proteins responsible for adhering the cells to the walls of the culture vessels.
- Proteomics research to study protein sequence and structure by digesting proteins into various peptides and/or amino acids.
- Breaking down casein, which is the protein found in milk.
- Tenderizing or texturing meat.
- Producing hypoallergenic food by digesting the allergen proteins that cause food allergies. This is commonly done with milk to reduce the incidence of babies developing milk allergies.
- Applications in veterinary medicine for wound care to remove dead tissue and/or pus from animals.
How do I reconstitute and store Trypsin?
Reconstitute trypsin in 1 mM hydrochloric acid (HCl; pH 3). Under these conditions, the enzyme is stable for approximately 1 year when properly aliquoted to avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles and stored at -20C. Adding calcium at 20 mM will benefit the enzyme stability by slowing trypsin’s ability to self-digest itself (autolysis).
Trypsin retains most of its activity in 2.0 M guanidine HCl, 0.1% SDS and 2.0 M urea. However, it becomes reversibly denatured above pH 11, by high concentrations of urea (> 6.5M) or precipitation with tricarboxylic acid (TCA).RE
What can inhibit trypsin activity?
Serine protease inhibitors will inhibit trypsin. These include aprotinin, Silver ion, EDTA, benzamidine, TLCK, various protein trypsin inhibitors isolated from egg white, lima bean, soybean, and pancreas.
Trypsin Enzyme from Porcine or Bovine pancreas
IntegriZyme’s Dr. Randy Meyer has nearly a decade of experience with trypsin and chymotrypsin and developed a novel, proprietary method of chromatographically purifying these enzymes. We have the capability of purifying these enzymes at different activity levels and mixtures of trypsin and chymotrypsin. We can produce USP grade trypsin as well as enzyme with 15,000- 20,000 BAEE units/mg from either bovine or porcine origin–at attractive, manufacturer-direct prices.
Let us know how we can help you with your trypsin project.
IntegriZyme, LLC isolates and purifies trypsin enzyme in the U.S. from U.S.-sourced animals.
It is available for purchase in 1, 10, 100, and 1000 g bottles or we can custom package in sizes to fit your needs. Please inquire.
Trypsin Specification (CAS 9002-07-7; EC 3.4.21.4)
Porcine Trypsin
Bovine Trypsin- Available Soon
Form: Liquid or Lyophilized Powder
Form: Liquid or Lyophilized Powder
Storage: -20C
Storage: -20C
Product activity options:
Product activity options:
Unit Definition: One USP [BAEE] unit will produce a delta A253 of 0.003 per minute at pH 7.6 at 25°C using BAEE as a substrate. (One BAEE unit will produce a delta A253 of 0.001 per minute at pH 7.6 at 25°C using BAEE as a substrate.)
≥ 250 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 750 BAEE Units/mg solid). Approximately 100 Units/mg chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 250 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 750 BAEE Units/mg solid). Approximately 100 Units/mg chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 1000 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 3000 BAEE Units/mg solid). (Approximately 400 Units/mg of chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 1000 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 3000 BAEE Units/mg solid). (Approximately 400 Units/mg of chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 2500 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 7500 BAEE Units/mg solid). Less than 5% chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 2500 USP [BAEE] Units/mg solid (≥ 7500 BAEE Units/mg solid). Less than 5% chymotrypsin (Or per customer specification).
≥ 4500 USP [BAEE] Units/mg protein (≥ 13,500 BAEE Units/mg ). Less than 5% chymotrypsin ( Or per customer specification).
≥ 4500 USP [BAEE] Units/mg protein (≥ 13,500 BAEE Units/mg ). Less than 5% chymotrypsin ( Or per customer specification).
Custom: : Let us know what you are looking for. We have the unique capability to consistently produce various trypsin products according to your specifications. Give us a call to discuss your product needs.
Custom: : Let us know what you are looking for. We have the unique capability to consistently produce various trypsin products according to your specifications. Give us a call to discuss your product needs.
For research, laboratory. and manufacturing use only. Not for drug or other use.